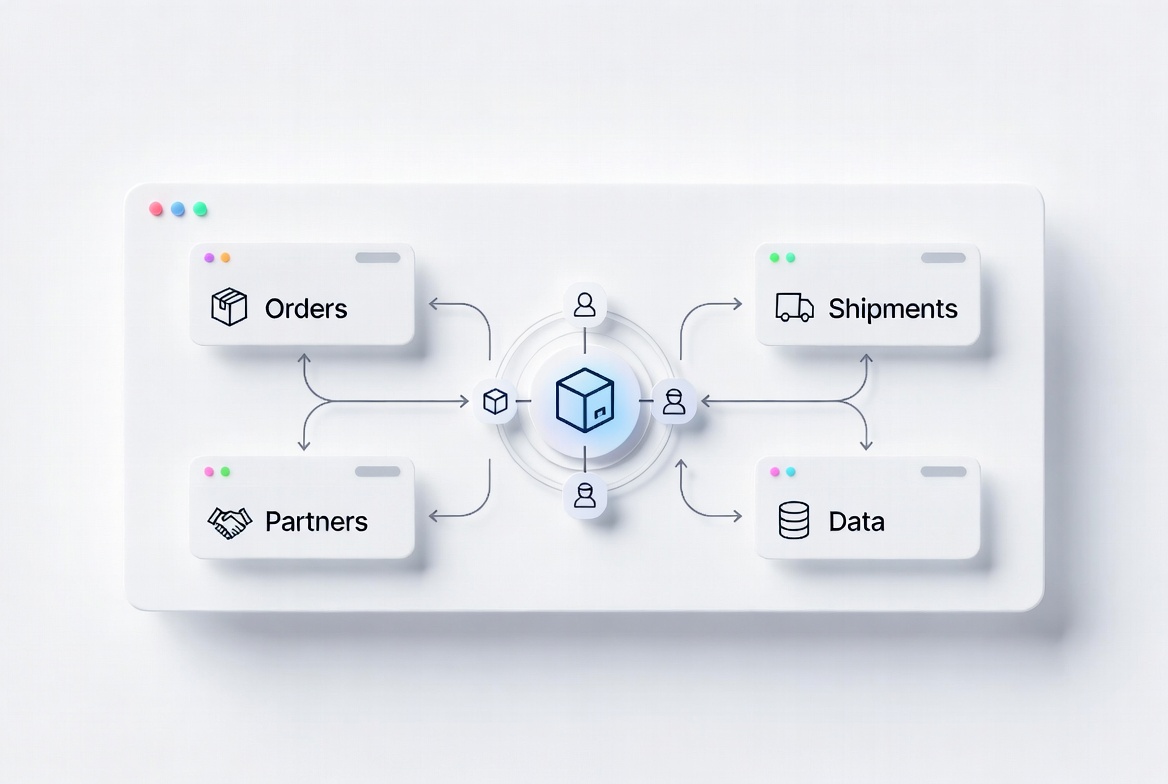
A logistics management system works by connecting orders, shipments, partners, and operational data into a unified workflow. It standardizes logistics processes from job creation to delivery tracking. By centralizing coordination and visibility, it reduces manual communication and improves execution efficiency.
Modern logistics operations involve multiple stakeholders, regions, and transport modes. A structured system ensures that all processes are executed consistently and transparently.
Core Workflow of a Logistics Management System
A logistics management system typically follows a standardized operational lifecycle. While specific implementations may vary, the core workflow remains similar across logistics organizations.
1. Order or Job Creation
The process begins when an order or shipment job is created in the system. This may originate from a customer request, an integration with another platform, or internal planning.
The system captures key data such as shipment details, service requirements, routing information, and partner assignments.
2. Shipment Planning and Execution
Once the job is created, the system supports shipment planning and execution. This includes assigning transport modes, coordinating with carriers, and defining operational milestones.
Execution activities are structured within the system to ensure consistency and traceability.
3. Partner Coordination
Logistics operations often involve carriers, agents, warehouses, and customs partners. A logistics management system enables coordinated communication and task management across these stakeholders.
Instead of relying on fragmented emails or spreadsheets, all parties interact through structured workflow updates.
4. Milestone Tracking and Status Updates
Shipment milestones such as departure, arrival, customs clearance, and delivery are tracked within the system.
Status updates are recorded and synchronized in real time, creating a continuous visibility layer across the shipment lifecycle.
5. Reporting and Operational Analysis
All shipment data is stored within the system and can be used for reporting and performance evaluation.
Operational dashboards provide insights into shipment volumes, service performance, and workflow efficiency, enabling continuous optimization.
Why Standardized Workflows Matter in Logistics Operations
Logistics operations can become complex as shipment volumes increase and partner networks expand. Without standardized workflows, companies often rely on manual coordination, leading to delays and inconsistencies.
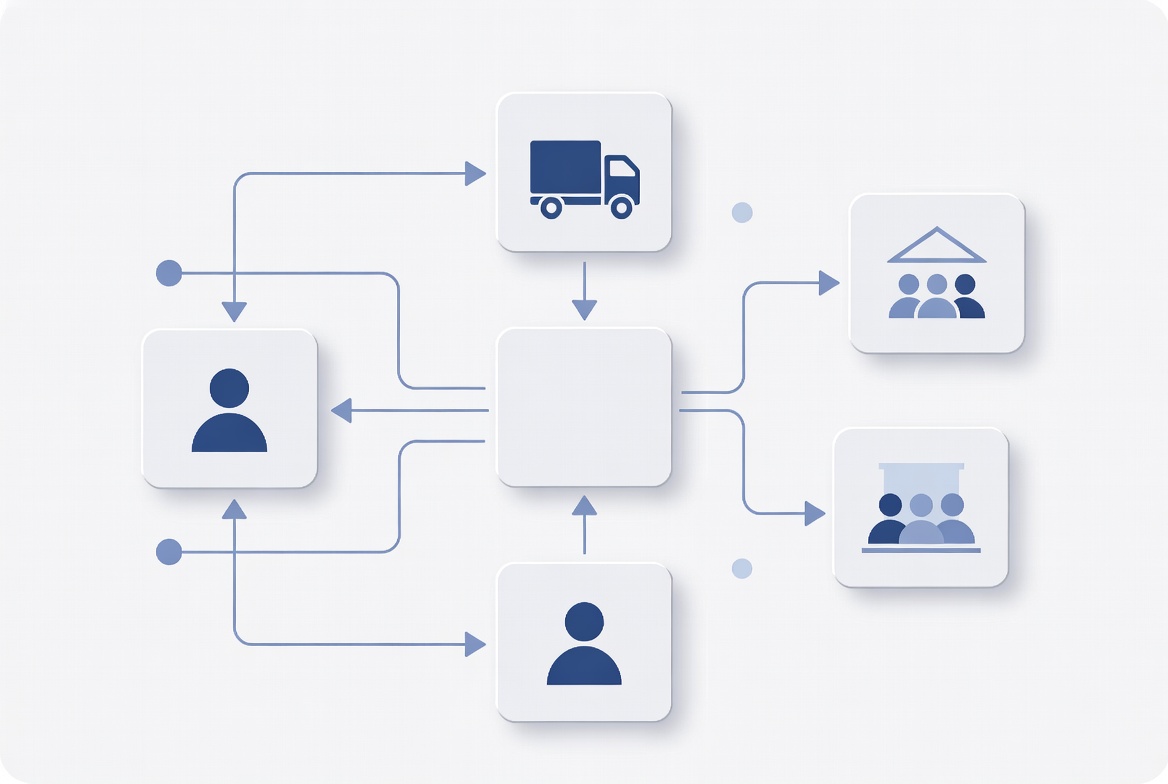
A logistics management system introduces structure by:
Defining repeatable process steps
Centralizing shipment data
Reducing dependency on manual communication
Improving operational transparency
This structure enables logistics companies to scale operations while maintaining control and visibility.
How This Differs from ERP or Transportation-Only Systems
Unlike enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems that focus on finance and administration, a logistics management system is designed specifically for logistics execution.
Unlike transportation-only systems, it covers broader operational workflows beyond carrier planning.
For a detailed comparison, see:
→ ERP vs logistics management system
→ TMS vs logistics management system
Explore logistics system use cases
Learn how logistics teams implement structured workflows





.webp)



